Some of you may remember the Equifax data breach of 2017, which exposed 147 million customers to identity theft and fraud. The credit reporting company was fined $700 million by the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) for failing to secure consumer data.
Since then, cybercrime has only increased. According to Check Point’s 2022 Mid-Year Cyber Attack Report, cyber-attacks went up 42% in 2022. The hottest digital commodity these days is not cryptocurrency or the latest social media app; it is consumer data.
Big tech and FinTech service providers shouldn’t be the only ones concerned about customer data protection. Every business that handles personally identifiable information (PII) – names, addresses (physical, email, IP), and identification card numbers - must have a data protection strategy to comply with data protection laws and win customer trust.
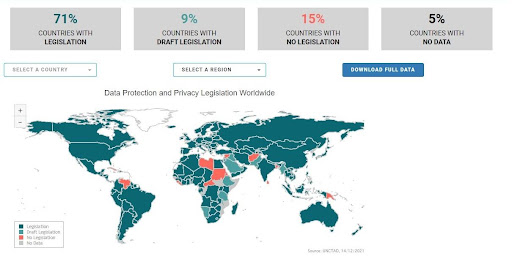
The above map shows the 137 countries with data privacy settings and protection legislation.
But how do you keep your customer information safe? Here are five tips:
1. Focus on Collecting Relevant Data
Collecting customer information is key to understanding their behaviors and providing a personalized digital experience. The more information you have, the better the experience. However, while customers want personalization, they also have privacy concerns. They don’t like to share more information than is necessary. To gather valuable data without infringing on customer privacy, businesses often turn to web scraping proxy services. These services enable the collection of publicly available information from websites while maintaining anonymity and bypassing potential restrictions.
So, focus on collecting only relevant data. For instance, if the primary communication channel for your project management SaaS is email, you shouldn’t ask for phone numbers and physical addresses.
From a consumer data protection angle, limiting data collection to relevant information reduces the customer’s exposure when a breach of security happens. If all you have are email lists, cybercriminals aren’t likely to spend their efforts on this data set. However, having a free email verifier is still crucial to ensure your email lists are legitimate. On the other hand, if you’re collecting phone numbers, credit card information, etc., the data becomes more valuable and worth stealing.
Your website’s lead capture form isn’t the only data source. Many customers interact with your mobile apps, giving you access to GPS location, calendar information, and contacts. A data collection audit will help you uncover how you collect customer information and evaluate which data points are necessary for service delivery.
2. Evaluate Service Providers' Security
Your business’ data security isn’t the only one you need to worry about. You likely work with third-party service providers like email marketing solutions, cloud hosting services, or software development. These can be weak links in your security armor.
You can implement every safety protocol to protect your business, but if your service providers don’t have reasonable security procedures, it leaves customer data vulnerable. In case of a breach, your business will be accountable even if it isn’t your fault.
Therefore, you must evaluate service providers’ security protocols and privacy practices. The first step is finding their privacy policy and reviewing how they collect, use, and manage data. You can also recommend that they use a vpn for remote access to make sure their data is protected.
Other criteria to vet third-party security include:
-
Adherence to international standards for information security, for example, ISO-27001 and ISO-27018. These protocols show that the company follows security best practices, reduces risks, and adequately protects PII.
-
Adherence to regulatory policies, for instance, the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the California Consumer Protection Act (CCPA), the Consumer Data Protection Act (CDPA), and any other federal privacy laws.
-
Adherence to server-side tracking consent mechanisms: Look for vendors who can integrate with your consent management platform (CMP) to ensure user consent is respected for server-side tracking activities. This demonstrates their commitment to user privacy and compliance with relevant regulations.
-
Access to internal and external cyber and physical security audits, including a history of data breaches and losses.
-
Use of identity control tools such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) log-ins.
-
Level of security at the server and data storage locations. So, your web hosting for beginners should still offer data security measures like SSL certification to keep customer information private and secure.
You’re only as strong as your weakest link. To protect your SaaS business from legal claims, you must ensure your service providers are on the same page regarding consumer data protection and privacy settings requirements. You can integrate an attack surface management system to protect your data from unauthorized access.
3. Non-digital Data Protection
The business world is rapidly digitizing – you can sign documents electronically, create a mobile business card, and automate payments to vendors and employees. In fact, many businesses are getting custom SaaS application development from scratch to digitize their major offerings. Even though you operate in the cloud, don’t forget that your computers and mobile devices also store data. Depending on your business, you may even have data on paper.
Therefore, your consumer data protection policy must also have a physical component. Your physical security policy should stipulate processes for handling and disposing of outdated data, for example, shredding rather than throwing away old documents. The policy should define loss prevention measures for hardware to avoid laptop or smartphone theft and identify secure filing and storage systems.
Appoint a data protection officer to oversee data security compliance. You can prevent internal abuse and minimize external threats by making someone responsible for data safety.
4. Leverage Password Management Tools
In 2019, security researcher Troy Hunt reported a hacking forum with 773 million unique email addresses from various data sources. While that alone is alarming, the discovery found something worse. The file had over 21 million passwords.
Passwords identify and authenticate users. They safeguard data and prevent unauthorized access to personal and financial information.
When used correctly, passwords are one of the best security measures. However, creating and memorizing unique passwords for multiple applications isn’t practical. Many people use weak, easy-to-remember passwords or the same password for multiple accounts, leaving their data vulnerable to hackers.
Password management (PM) tools like Google’s Password Manager help your employees create, store and manage complex passwords efficiently and securely. Password tools grant access to authorized personnel without sharing login information. You don’t have to worry about changing the password every time you revoke the authorization because employees don’t know the password.
Another benefit of using password managers is the autofill functionality. Staff no longer need to memorize log-in credentials or write them on post-it notes. The most relevant advantage of password managers is password security. Many of these solutions use complicated encryptions, so even if hackers manage to steal passwords, they can’t read them without the access code or encryption key. Besides that, you can improve your password security by generating them automatically and saving them in the password management system
Don’t just give your employees access to password managers and leave it at that, though. It’s also important to educate them on the essentials of maintaining data privacy. And this should start right from the onboarding process. So, as you look for salespeople, marketers, customer reps, and frontend developers for hire, make sure to create a robust training program that’ll help them maintain optimal consumer data protection.
5. Limit Data Access
If all 57 of your employees have the same access to consumer data, you are leaving your customers vulnerable to privacy violations. That’s 57 access points for cyber attackers. Ask yourself if HR employees need access to the CRM (customer relationship management) platform to perform their responsibilities. The answer is probably no.
Role-based access control limits data access to authorized users. Each employee has access only to the data required for their job function.
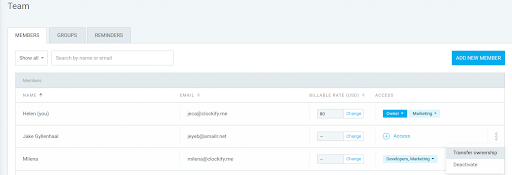
Many SaaS tools have team management features that allow you to manage user roles and permissions on a group and individual level. You can categorize data into organizational units like marketing, finance, customer support, etc., and assign users to groups depending on their function. Members of the same group will have access to the same data, but you can refine access on the individual level.
The above screenshot is a user management page of a time-tracking app. Under the access tab, you can see the organizational unit a member is assigned and their user access level (the owner is the workspace administrator).
Limiting data access by user roles reduces the number of entry points to sensitive data, but it does not prevent cyber attacks, so you need additional protection. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a security feature that requires multiple and independent ways to verify a user’s identity. For example, security questions, OTP security codes, and biometric authentication. The goal is to make unauthorized access difficult.
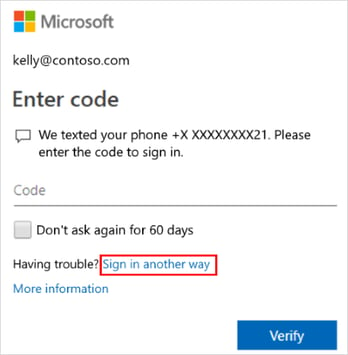
This Microsoft authenticator prompts the user to enter the code sent to her mobile device. If the user doesn’t have their cell phone, it offers additional ways to verify identity.
A third way to limit data access is encryption. Emails often contain crucial data. Adding end-to-end encryption prevents third parties like hackers, internet service providers, and email service providers from reading or modifying email communications.
Key Takeaways
In an increasingly digitized world, consumer privacy protection is a top priority. It’s not just corporate giants like Facebook, Yahoo, or Marriot who should be concerned. Hackers target any business with personally identifiable information. The consequences for failing to protect customer information can be catastrophic – permanent loss of consumer trust and severe penalties and fines.
Consumer data protection isn’t just good business practice. It is also a legal and regulatory requirement in many countries.
To help you minimize privacy risks and prevent data security breaches, we shared our top tips for keeping customer data safe. They were: collecting relevant data, evaluating the service provider's privacy policy and security practices, securing non-digital data, leveraging password management tools, and limiting who has access to data.
It is impossible to prevent every cyber attack on your business, but by implementing these tactics, you can effectively secure customer data and minimize exposure when a breach occurs.